Go/Leet Code
[Go]Array and String - Implement strStr()
Gopythor
2022. 4. 4. 23:09
728x90
반응형
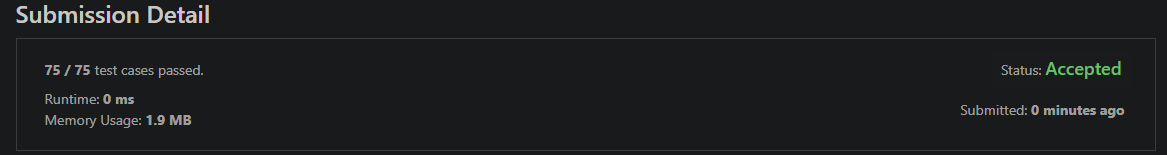
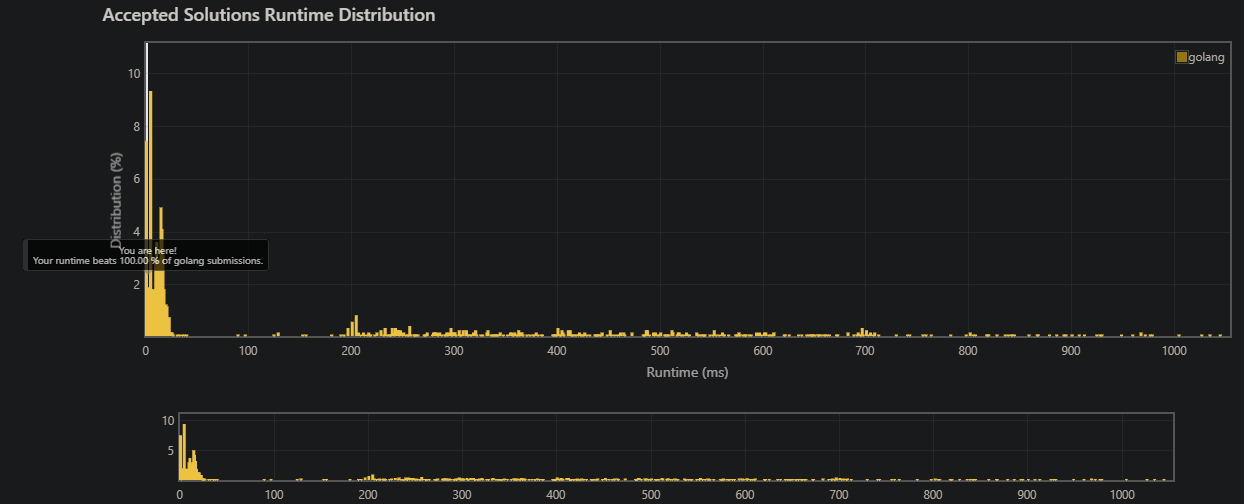
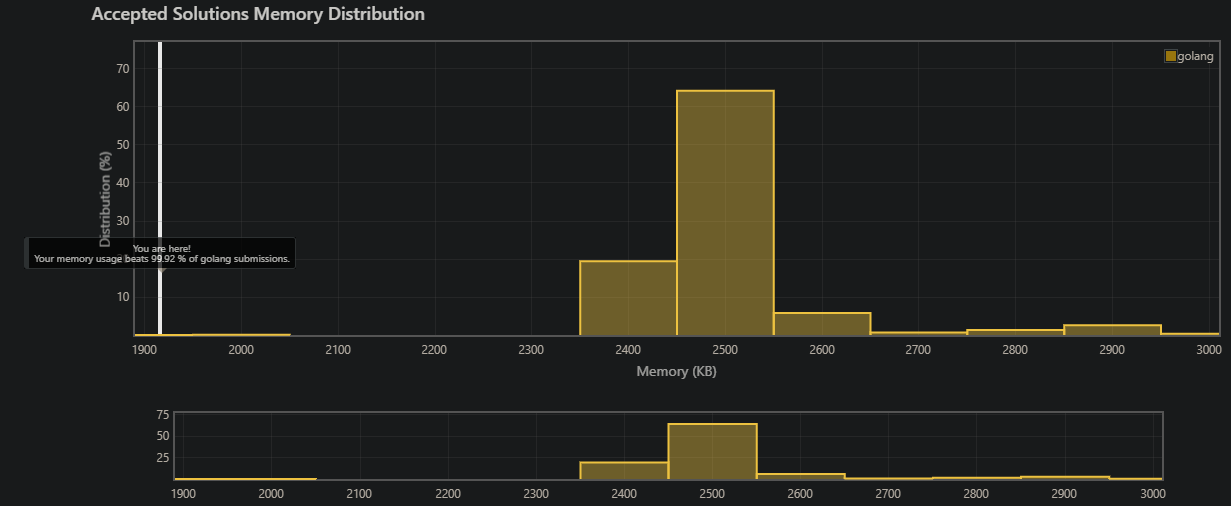
Implement strStr().
Given two strings needle and haystack, return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle is not part of haystack.
Clarification:
What should we return when needle is an empty string? This is a great question to ask during an interview.
For the purpose of this problem, we will return 0 when needle is an empty string. This is consistent to C's strstr() and Java's indexOf().
Example 1:
Input: haystack = "hello", needle = "ll"
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: haystack = "aaaaa", needle = "bba"
Output: -1
Constraints:
- 1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 104
- haystack and needle consist of only lowercase English characters.
My code(
func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
return strings.Index(haystack, needle)
}- This code is so simple, but I think it doesn't help my coding skill.
https://go.dev/play/p/SfKM7c6aJbB
func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
if len(haystack) < len(needle) {
return -1
}
needler := []rune(needle)
haystacker := []rune(haystack)
for i, v := range haystacker {
if v == needler[0] {
if len(needler) == 1 {
return i
}
for j := 0; j < len(needler); j++ {
if i+len(needler) > len(haystacker) {
return -1
}
if haystacker[i+j] != needler[j] {
break
} else if j == len(needler)-1 {
return i
}
}
}
}
return -1
}- I implemented this code again.
- I made edge case when needle is longer than haystack.
- To compare, string converts to rune.
- For loop will run during finding needle value of array[0]
- When length of needler is 1, it will return i right away.
- After passing needler length check, for loop will run until end of value of needler.
- when matching all, it will return i, if not, break will happen.
- If for loop cannot find if conditions, it will return -1.
https://go.dev/play/p/4NYEN5nRbVG
sample 0 ms submission
func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
for c := range haystack {
i, j := c, 0
for i < len(haystack) && j < len(needle) {
if haystack[i] != needle[j] {
break
}
i++
j++
}
if j == len(needle) {
return c
}
}
return -1
}- This code looks simple.
- For loop will run from start to end of array.
- variables i and j will have c which is index of haystack and 0.
- After allocating variables, for loop will run when i is not same or greater than haystack length and j is not same or greater than needle.
- during comparing i with b, if they do not match, for loop will break.
- if they match, i and j will be checked until end of array.
- if j is same with length of needle then c will be returned or not -1 will be returned.
sample 1 ms submission
func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
h := make(map[string]bool)
h[needle] = true
index := 0
if needle == "" {
return index
} else {
for index < len(haystack) {
if haystack[index] == needle[0] {
if len(haystack) < index + len(needle) {
return -1
}
tempS := haystack[index:(index + len(needle))]
if _, ok := h[tempS]; ok {
return index
}
}
index++
}
return -1
}
}- h map will be made with string key and bool value.
- h [needle] in map has true.
- Because map in go is hash table, so there will not be duplicated value.
- needle is a valuable so key will be allocated its value ex) needle = "pic", h["pic"]=true
- It is not important value is bool or not.
- index will be 0
- I don't know why if condition checks needle is "". Without it, code works
- for loop will run until index has same value with length of haystack.
- In for loop, if condition checks haystack[index] and niddle[0]
- when added value of index and length of needle is greater than length of haystack, it will return -1.
- tempS will have a value which haystack[index : index + len(needle)]
- after that, if condition checkes tempS exists in map or not.
- When it couldn't find key, then index increase.
sample 3 ms submission & sample 2000 KB submission
// 28. Implement strStr()
// time: O(n)
// space: O(1)
func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
k := len(needle)
if k == 0 {
return 0
}
n := len(haystack)
start := 0
for start < n {
pIdx := 0
sIdx := start
for pIdx < k && sIdx < n && haystack[sIdx] == needle[pIdx] {
sIdx++
pIdx++
}
if pIdx == k {
return start
}
start++
}
return -1
}- I think this code is almost same with 0ms submission.
- I don't think edge case checker doesn't need.
- but different is that for loop in this code also checks if value is same between haystack and needle.
sample 4 ms submission & sample 2500 KB submission
func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
if needle == "" {
return 0
}
for i := 0; i < len(haystack); i++ {
if len(needle)+i > len(haystack) {
return -1
}
if haystack[i:(len(needle)+i)] == needle {
return i
}
}
return -1
}- I think this code is good to study.
sample 2600 KB submission
func strStr(haystack string, needle string) int {
res:=""
for i:=0;i<len(haystack)-len(needle)+1 && i >= 0; {
//fmt.Println("i", i, len(word))
res=haystack[i:i+len(needle)]
if res==needle{
return i
}
i++
}
return -1
}728x90
반응형