고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
728x90
반응형


Given an integer rowIndex, return the rowIndexth (0-indexed) row of the Pascal's triangle.
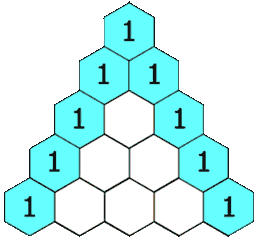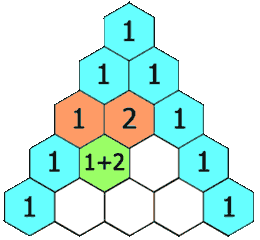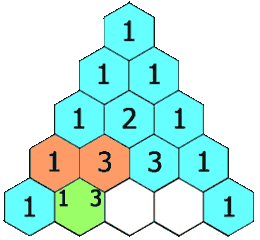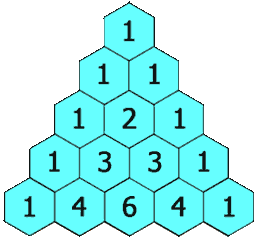
In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it as shown:
Example 1:
Input: rowIndex = 3
Output: [1,3,3,1]
Example 2:
Input: rowIndex = 0
Output: [1]
Example 3:
Input: rowIndex = 1
Output: [1,1]
Constraints:
- 0 <= rowIndex <= 33
Follow up: Could you optimize your algorithm to use only O(rowIndex) extra space?
My code
func getRow(rowIndex int) []int {
rowIndex++
pa := make([][]int, rowIndex)
for i := 0; i < rowIndex; i++ {
pa[i] = make([]int, i+1)
pa[i][0], pa[i][i] = 1, 1
for j := 1; j < len(pa[i])-1; j++ {
if i > 1 {
pa[i][j] = pa[i-1][j] + pa[i-1][j-1]
}
}
}
re := make([]int, rowIndex)
copy(re, pa[rowIndex-1])
return re
}- rowIndex is used as a variable which is like a array address of row index.
- So it will be increase by 1(normally forloop takes condition which less than length(it doesn't care about start of array[0].
- When rowIndex is 0, lt would be 1 for forloop so that we can get result as expected.
- pa will be 2 demensional array.
- In for loop, row will be created based on rowIndex variable.
- For creating column, Variable i will be added by 1.
- The value of start and end array will be 1 and I implement one line for reducing for loop resource.
- Next for loop will start from 1 to length-1 of array for allocating values which are the results of addition of former row.
- if condition checks if i is greater than 1. because there is no space for addition result.
- end of for loop, re slice will be made for return 1d slice.
https://go.dev/play/p/LK-SEl3SxM2
Go Playground - The Go Programming Language
About the Playground The Go Playground is a web service that runs on go.dev's servers. The service receives a Go program, vets, compiles, links, and runs the program inside a sandbox, then returns the output. If the program contains tests or examples and n
go.dev
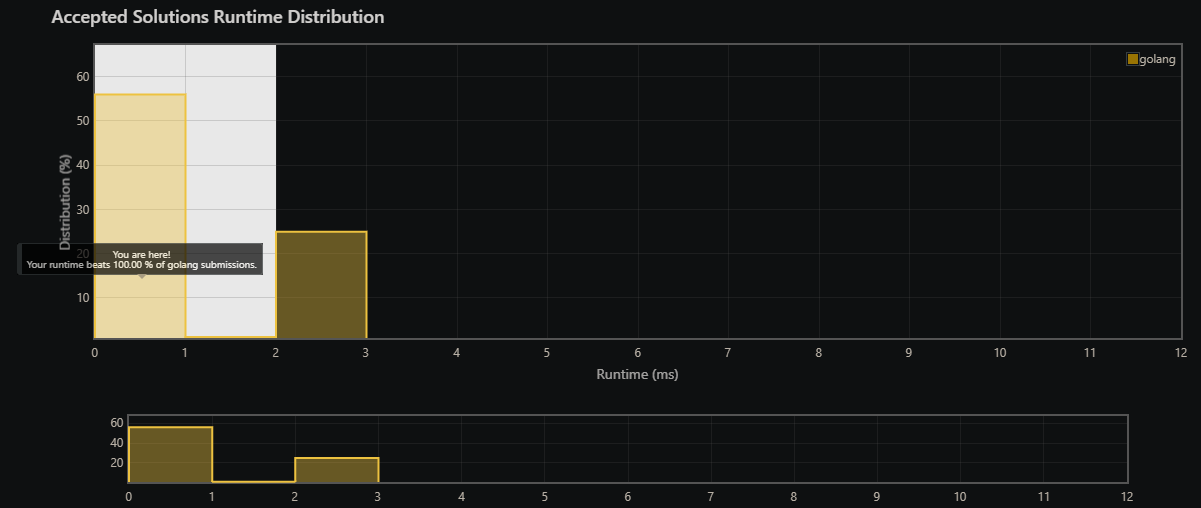
sample 0 ms submission & sample 1900 KB submission
func getRow(rowIndex int) []int {
prev := make([]int, 1)
prev[0] = 1
if rowIndex == 0 {
return prev
}
row := 0
for {
row++
arr := make([]int, row + 1)
arr[0] = 1
arr[row] = 1
for ind := 1; ind < row; ind++ {
arr[ind] = prev[ind - 1] + prev[ind]
}
prev = arr
if rowIndex == row {
break
}
}
return prev
}- This code used 1d array. maybe 2d array is not necessary for it.
- But this code uses prev and arr slice.
- prev will be initialzied to size 1 array with value 1.
- when rowIndex is 0, it will be return. but when is more, row will be initialzed to 0.
- row will increase and arr will be made with row+1.
- arr 0, end of array will have 1.
- for loop will run during ind reaches to row.
- prev has previous array value, so it can be calculated.
- after calculation, prev will have arr.
- and it will be return when row reaches to rowIndex.
sample 1 ms submission
func getRow(n int) []int {
row := []int{1}
for k := 1; k <= n; k++ {
row = append(row, row[len(row)-1] * (n - k + 1)/k)
}
return row
}- This code is so simple, I need to learn it also.
sample 2 ms submission
func getRow(rowIndex int) []int {
arr := make([] int, rowIndex+1)
arr[0] = 1
for i := 0 ; i <= rowIndex ; i++ {
for j := i ; j > 0 ; j-- {
arr[j] += arr[j-1]
}
}
return arr
}- This code is also looks complicated and simple.
sample 2000 KB submission
func getRow(rowIndex int) []int {
rs := make([]int, rowIndex + 1)
if rowIndex >= 0 {
rs[0] = 1
}
if rowIndex >= 1 {
rs[0] = 1
rs[1] = 1
}
if rowIndex <= 1 {
return rs
}
for i := 2; i <= rowIndex; i++ {
rs[i] = 1
for j := 1; j <= i / 2; j++ {
rs[i - j] = rs[j - 1] + rs[j]
}
for j := 1; j <= i / 2; j++ {
rs[j] = rs[i - j]
}
}
return rs
}sample 2100 KB submission
func getRow(rowIndex int) []int {
res := make([][]int, rowIndex+1)
res[0] = []int{1}
for i := 1; i <= rowIndex; i++ {
res[i] = make([]int, i+1)
res[i][0] = 1
res[i][i] = 1
for j := 1; j < i; j++ {
res[i][j] = res[i-1][j-1] + res[i-1][j]
}
}
return res[rowIndex]
}sample 2200 KB submission
func getRow(rowIndex int) []int {
result := [][]int{[]int{1}, []int{1, 1}}
row := []int{}
if rowIndex == 0 {
return result[0]
}
if rowIndex == 1 {
return result[1]
}
for i := 2; i <= rowIndex; i++ {
prevArray := result[i-1]
leftIdx := 0
rightIdx := 1
current := []int{1}
for leftIdx < rightIdx && rightIdx < len(prevArray) {
left := prevArray[leftIdx]
right := prevArray[rightIdx]
current = append(current, left+right)
leftIdx += 1
rightIdx += 1
}
current = append(current, 1)
row = current
result = append(result, current)
}
return row
}
728x90
반응형
'Go > Leet Code' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Go] Array and string - Reverse Words in a String III (0) | 2022.04.16 |
|---|---|
| [Go] Array and string - Reverse Words in a String (0) | 2022.04.16 |
| [Go] Array and string - Rotate Array (0) | 2022.04.14 |
| [Go] Array and String - Minimum Size Subarray Sum (0) | 2022.04.13 |
| [Go] Two-pointer Technique - Scenario II (0) | 2022.04.12 |





댓글 영역